Ostarine UK - SARM
CAS : CAS 841205-47-8
Supplied in : 10mg Pellet x 90
Specification : ≥ 99.36%
CAS : CAS 841205-47-8
- Download MSDS
- Download Certificate of Analysis (COA)
- Research Use Only
10mg x 90 Pellets £39.99
Information
- Safety & Handling
- Ordering Process
- Storage Information
Ostarine Chemical Profile
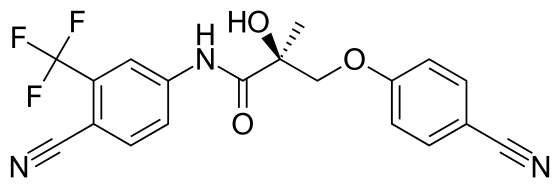
Basic Chemical Structure:
- Molecular Formula: C19H14F3N3O3 [Verify on Pubmed]
- Molecular Weight: 389.33 g/mol
- Classification : SARMS UK
Structural Features:
- Core Structure: The backbone of Ostarine includes a phenyl ring substituted with a cyano group (CN) and a trifluoromethyl group (CF3), which are critical for its activity and selectivity.
- Linkage: Attached to this phenyl ring is a hydroxymethylpropanamide moiety, a component that plays a crucial role in its binding affinity to the androgen receptor.
- Attachment: The molecule also contains an ether linkage with a phenoxy group, which has additional substituents, enhancing its pharmacokinetic properties such as solubility and stability in biological environments.
Functional Groups and Their Implications:
- Cyano Groups (CN): The presence of cyano groups in Ostarine contributes to its strong binding affinity and selectivity towards androgen receptors. Cyano groups can improve the drug’s stability and its interaction with the target receptor.
- Trifluoromethyl Group (CF3): This group enhances the molecule’s lipophilicity, which can influence its absorption and distribution within the body, potentially increasing its efficacy at target sites.
- Ether and Phenoxy Linkages: These components affect the overall polarity of the molecule, influencing its solubility and its ability to permeate cell membranes.
Stereochemistry:
- Ostarine has specific chiral centers that affect its interaction with androgen receptors. The stereochemistry at these centers can dictate the direction and strength of the binding to the receptor, thereby influencing the drug’s effectiveness and safety profile.
Biological Activity:
The detailed structure of Ostarine allows it to mimic the action of testosterone by binding to androgen receptors selectively, thereby stimulating anabolic activities like muscle growth and bone preservation without many of the side effects associated with conventional anabolic steroids.
Ostarine Information
Molecular Structure and Mechanism of Action:
Ostarine binds to the androgen receptor (AR) with high affinity and selectivity. Structurally, it is quite different from classical steroids, exerting a predominant anabolic action on muscles and bones while decreasing unwanted androgenic effects on other tissues of the body, including the prostate and scalp.
Molecular interaction of Ostarine with the AR makes the alteration in the conformation of the receptor, resulting in selective transcription of genes leading to protein synthesis and muscle growth.
Clinical Implications and Therapeutic Potential
Human trials of ostarine have shown that it is effective for increasing lean body mass and improving physical function in a range of populations, such as patients suffering from cachexia due to cancer and those with age-related muscle loss. The action of Ostarine is site-specific and will, therefore, support muscle hypertrophy and hyperplasia with the preservation of bone, and may prove itself worthy to be used as a dual-action agent in the fights against osteoporosis and sarcopenia.