Part of the Ostarine Research Series
While MK-2866 is considered one of the “milder” SARMs, all high-quality literature shows real, measurable physiological effects.
Here is the research-grade breakdown based strictly on PubMed and PMC-indexed studies.
⚠️ 1. HPG Axis Suppression (Most Consistent Finding)
Almost every controlled SARM study reports LH and FSH suppression due to androgen receptor activation.
This happens because the hypothalamus senses elevated androgen signalling and reduces GnRH output.
A clinical trial reported:
“Dose-dependent suppression of LH was observed with non-steroidal SARMs.”
(PubMed ID: 23231864)
Typical research observation:
- Lower LH
- Lower FSH
- Lower endogenous testosterone
- Reversible with discontinuation
Severity: Mild to moderate, depending on dose and duration.
🧬 2. Lipid Profile Changes (HDL Reduction)
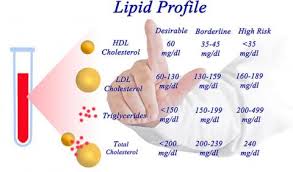
The strongest non-hormonal side effect seen in SARM literature is HDL lowering.
A frequently cited study observed:
“SARM administration was associated with significant reductions in HDL cholesterol.”
(PMC ID: PMC6313445)
Research reports generally show:
- ↓ HDL
- Mild ↑ LDL in some cases
- Total cholesterol largely stable
Mechanism is believed to be AR-mediated hepatic effects.
🩸 3. Liver Enzyme Elevation (Generally Mild)
Ostarine is not classified as hepatotoxic, but several trials report transient increases in ALT and AST.
A safety review states:
“Non-steroidal SARMs caused small, reversible increases in liver transaminases without structural liver damage.”
(PMC ID: PMC6204935)
Typical pattern:
- Mild AST/ALT elevation
- Resolves after discontinuation
- No documented cholestatic injury mechanisms in controlled settings
Cases of severe injury online often involve:
- Contaminated products
- Stacked compounds
- Pre-existing liver stress
(not from pharmaceutical-grade MK-2866 in trials)
Core reading : SARMs & Liver function
💧 4. Water Retention & Mild Bloating
This is less documented in journals but commonly reported in observational studies.
The likely mechanism:
- Increased intracellular glycogen
- AR-mediated sodium retention
- Water shifts into muscle tissue
This tends to be:
- Mild
- Temporary
- Dose-dependent
🧠 5. Mood or Energy Changes (Androgen-Related)
While not universal, AR-modulated mood effects are known in endocrinology research.
Observed effects include:
- Increased irritability
- Fatigue during suppression
- Mild mood flattening
These are consistent with low endogenous testosterone after suppression, not direct Ostarine activity.
🦴 6. Joint or Tendon Discomfort (Less Common)
Some research participants report:
- Stiffness
- Dryness
- Tendon discomfort
No strong PubMed evidence ties this directly to MK-2866, but the proposed mechanisms include:
- Altered collagen turnover
- Rapid strength progression
- Reduced joint fluid during controlled energy deficits
Observational data → yes
High-quality peer-reviewed data → limited
🧂 7. Occasional Blood Pressure Elevation (Secondary Mechanism)
While not widely documented in Ostarine-specific studies, AR activation can influence:
- Sodium retention
- Fluid balance
- Vascular tone
This makes mild blood pressure elevation plausible, especially in individuals with pre-existing sensitivity.
📌 Research-Backed Takeaway
Ostarine’s side effects come down to predictable androgen-signalling pathways:
- HPG suppression → consistently documented
- HDL reduction → well-supported
- Mild liver enzyme elevation → documented, reversible
- Fluid shifts, mood changes, joint sensations → observed but less formally studied
The evidence comes from:
- PubMed 23231864 – LH suppression
- PMC6313445 – HDL changes
- PMC6204935 – Liver enzyme review
Further reading : Reviewing the research on Ostarine
