-

Enclomiphene / 100 x 10mg
£49.90 — or subscribe and save 15% Add to cart -

MK-2866 (Ostarine) / 100 x 10mg
Rated 4.95 out of 5(21 customer reviews) £44.90 — or subscribe and save 15% Add to cart -

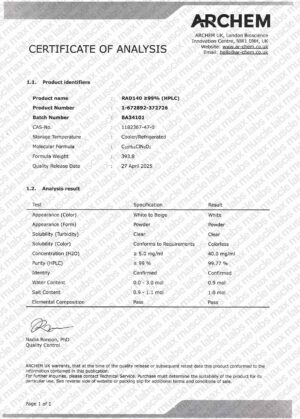
RAD140 / 100 x 10mg
Rated 5.00 out of 5(24 customer reviews) £49.90 — or subscribe and save 15% Add to cart -
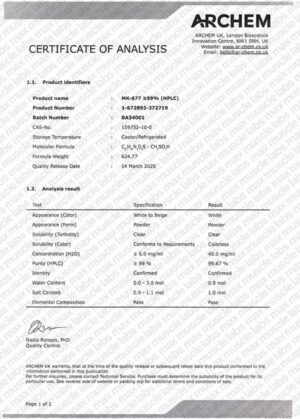
MK-677 (Ibutamoren) / 100 x 10mg
Rated 4.94 out of 5(34 customer reviews) £49.90 — or subscribe and save 15% Read more -

SR9009 (Stenabolic) / 100 x 10mg
Rated 5.00 out of 5(1 customer review) £49.90 — or subscribe and save 15% Add to cart -

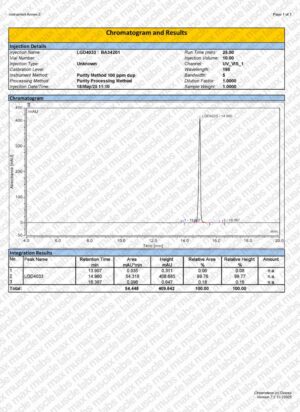
LGD-4033 (Ligandrol) / 100 x 10mg
Rated 5.00 out of 5(3 customer reviews) £49.90 — or subscribe and save 15% Add to cart -

AC-262536 / 100 x 10mg
Rated 5.00 out of 5(1 customer review) £49.90 — or subscribe and save 15% Add to cart -

GW0742 / 100 x 10mg
Rated 5.00 out of 5(1 customer review) £49.90 — or subscribe and save 15% Add to cart -

S-4 (Andarine) / 100 x 25mg
Rated 5.00 out of 5(4 customer reviews) £44.90 — or subscribe and save 15% Add to cart -

YK-11 (Myostine) / 100 x 10mg
Rated 5.00 out of 5(3 customer reviews) £54.90 — or subscribe and save 15% Add to cart -

SR9011 / 100 x 10mg
£54.90 — or subscribe and save 15% Add to cart -

RAD150 / 100 x 10mg
£49.90 — or subscribe and save 15% Add to cart -
ACP-105 / 100 x 10mg
Rated 5.00 out of 5(2 customer reviews) £59.90 — or subscribe and save 15% Add to cart -

LGD-3303 / 100 x 10mg
£49.90 — or subscribe and save 15% Add to cart -

MK-29 (OTR-AC) / 100 x 10mg
£44.90 — or subscribe and save 15% Add to cart -

S-23 / 100 x 10mg
Rated 5.00 out of 5(4 customer reviews) £44.90 — or subscribe and save 15% Add to cart
SARMS UK - Research Grade
SARMs (Selective Androgen Receptor Modulators) are synthetic compounds designed to bind selectively to androgen receptors in the body.
Unlike anabolic steroids, which activate receptors throughout many tissues, SARMs target specific areas — primarily muscle and bone — while avoiding others like the prostate or liver. Ostarine is prime example of this class.
This selective action allows researchers to explore anabolic effects (such as increased muscle mass or bone density) with reduced systemic side effects. SARMs are commonly studied in contexts like muscle wasting, osteoporosis, and hormonal regulation, but they remain investigational and are not approved for human consumption.
Moving in 2026 - New information available
Where to start : SARMs glossary
Need to check the law? SARMs law update for 2026
Check out our Buying Guide
SARMS - Compared
| Compound | Receptor Selectivity | Typical Research Range* | Half-Life | Key Research Observations | Distinctive Features |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ostarine (MK-2866) | High AR affinity (muscle/bone) | 1–3 mg/day | ~24 hours | Frequently analysed for lean mass and musculoskeletal studies | Most studied SARM in published literature |
| Ligandrol (LGD-4033) | Potent AR binding | 0.1–1 mg/day | ~24–36 hours | Phase I/II trials on strength and mass | Higher AR affinity vs MK-2866 |
| RAD-140 (Testolone) | Very high AR selectivity | 0.1–1 mg/day | ~16–24 hours | Explored for neuroprotection and bone effects | Strongest AR agonist in SARM category |
| Andarine (S-4) | Moderate AR selectivity | 25–50 mg/day | ~3–6 hours | Examined for muscle/bone pathways | Short half-life, often divided in studies |
| ACP-105 | Potent AR activation | 1–10 mg/day | ~4–6 hours | Strong signalling effects in rodent studies | Often compared to RAD-140 |
| S23 | Very strong AR selectivity | 0.5–5 mg/day | ~11–12 hours | Studied for male contraception models | Extremely potent; narrow research applications |
| YK-11 | Partial AR agonist (myostatin modulation) | 1–10 mg/day | ~6 hours* | Mostly in vitro/in vivo data | Hybrid steroidal-SARM mechanism |
| MK-677 (Ibutamoren)† | GH secretagogue (not a SARM) | 5–25 mg/day | ~6 hours | GH/IGF-1 axis signalling and sleep studies | Oral GH secretagogue |
| SR9009† | REV-ERB agonist (not a SARM) | 20–30 mg/day | ~2–4 hours | Circadian and metabolic research | Mechanistically unrelated to AR pathways |
*Research ranges reference published experimental literature — not guidance for human consumption.
† Not a SARM; included due to common comparison in research discussions.
Testing procedures
Third-Party Testing
Every Batch, No Exceptions
Every compound we supply comes with a batch-specific Certificate of Analysis (COA) from an accredited third-party lab. We use validated methods like HPLC and LC-MS/MS to confirm:
- Compound identity Purity (≥98%)
- Absence of contaminants or adulterants
You’ll always know exactly what you’re working with — no assumptions, no guesswork.
Professional Grade
Packaging and Fulfilment
Your order is handled like a research shipment should be:
- Sealed, tamper-evident containers
- Discreet, trackable delivery (Royal Mail, DPD)
Same-day dispatch on weekdays for most orders
We’ve designed every step of the process to protect compound integrity and researcher confidence.
UK Legislation Compliance
Safety handling compliance
Our SARMs are shipped with physical copies of the Material Safety Datasheet, and are labelled with the specific hazard classification for each compound.
Research supply only
We only supply our compounds to those involved in the research and development industry. Checks are undertaken to ensure correct possession and usage of our compounds
Next day UK SARMS delivery
& effective customs clearance
Royal Mail 24
We aim to ship stocked items within 24 hours of ordering, Monday to Friday
Customs Clearance
We have extensive experience in working with international customs to ensure the correct assessment and hassle-free import for your order
How We Maintain REACH Compliance for SARMs
Stock threshold control
We supply in small batches for laboratory use, well below the 1-tonne annual threshold that triggers mandatory REACH registration. This means formal registration is not currently required — but other obligations still apply.
Safe Handling, Packaging & Labelling
We ensure all research compounds are:
- Labeled with appropriate hazard warnings (GHS/CLP-compliant)
- Supplied with SDS (Safety Data Sheets) where applicable
- Packaged in a way that prevents leakage, degradation, or contamination

